Facial Growth and Airways
Stephen Deal • Dec 12, 2018

21st Century Orthodontics-Don’t Just Straighten Teeth… Increase Your Face Value!!!
As parents, we want what is best for our children in every way. Many parents are well aware of the specific milestones that our children should reach during the first eighteen months of life, however; there are several important growth and development factors that must be evaluated in each child during the first decade of life. Surprisingly, it is your child’s dentist who becomes the guardian of normal facial growth and development. The role of your dentist is more than just taking care of your child’s teeth. It is their goal to monitor and guide the growth and development of young children to achieve the following:
1. A Pleasing Face which equals Optimal Esthetics
2. A Beautiful “Full Smile”
3. A Normal and Functional Bite
4. No TMJ Problems
5. No Sleep Disordered Breathing
6. A Lifetime of Oral Health
Many parents are unaware that 60% of their child’s facial development is completed by the age of 8 and that 90% of facial development is completed by the age of 12. This means that the earlier your child sees a dentist, the better the opportunity to detect and correct any growth and development problems that may be present.
Facial growth is the sum of the individual growth of each bone which comprises the face. There are several influences which can cause an unequal growth of a child’s face and this imbalance may affect a child’s health and appearance. A normal balanced face is the result of more than just bone growth; it is the balance of normally functioning muscles, proper nutrition and the ability to breathe normally. Scientific literature and studies have shown that when these delicate balances are altered, changes in health and appearance occur.
One of the most common abnormalities in a child’s facial growth and development is caused by a compromised airway or quite simply stated – The inability to breathe properly through the nose. Children who cannot breathe well through their nose will tend to breathe through their mouth. This sets up a chain of events which may severely impact not only the health of a child, but also the way a child’s facial features develop, and ultimately the way a child looks as an adult. The most common causes of altered breathing are:
- Enlarged Adenoids
- Enlarged Tonsils
- Deviated Septum (Nasal obstruction)
- Allergies
- Chronic Sinus Infections
The effects of a compromised airway on the growth of a child are revealed in many ways. The tongue often positions itself snugly in the lower jaw to allow a child to breathe more readily through the mouth. This in turn changes the growth of the lower jaw so that it grows more vertically. This change in growth direction makes the child’s face grow longer. At the same time since nasal breathing is severely compromised, the upper jaw and midface (the nasal bones, cheek bones, and bones supporting the tissue of the face) fail to develop at a normal rate because the natural growth stimulant of air flow through the nose is absent. This results in a deficiency of growth of the upper jaw and midface, which added to the long facial growth from the lower jaw, directly impacts the facial balance and beauty of a child and later as an adult.
As parents we often see the signs of airway problems, however; they often go unnoticed. Here are a few common symptoms of airway problems:
- Mouth Breathing – Lips apart
- Chapped Lips and Soft Tissue Gingivitis
- Venous Pooling Beneath the Eyes – Dark circles beneath the eyes
- Change in Head Posture – Posturing the head forward and/or tipping the forehead backwards
- Tonsil and Adenoid Problems – Chronic sinus problems, throat problems
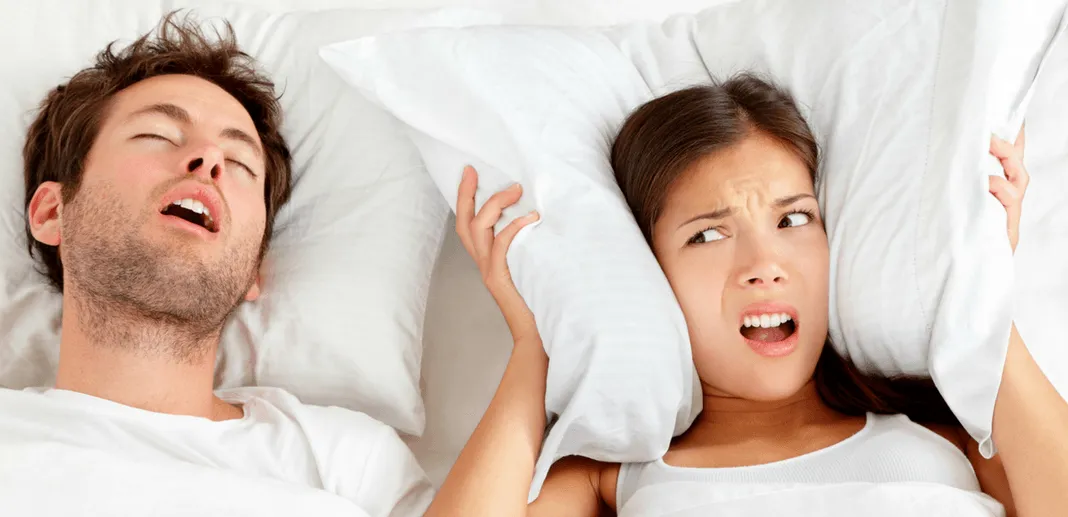
- Snoring – Children do not usually snore
- Loud grinding of teeth during sleep
- Bed wetting
- Reflux in the Eustachian Tube – Leads to inner ear infections
Enlarged adenoids and tonsils are one of the most common causes of airway compromise. Adenoids are tonsil-like glands located at the back of the nose. The most current literature indicates that tonsils and adenoids serve to bolster the immune system during the first two years of life. After that, there seems to be no obvious function and a child can live normally without them.
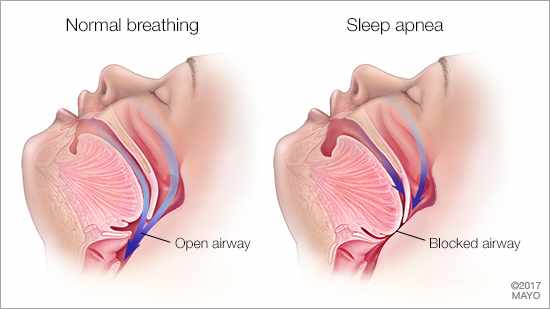
Children are born with adenoids which are quite small. As a child grows, so do the adenoids, reaching their maximum size when the child is 10 to 12 years old. From that point on, normal adenoid tissue starts to shrink on its own. It’s during the growth phase that adenoids can cause problems. Enlarged, or “hypertrophied” adenoids, can block a child’s nasal passages and result in nasal congestion, mouth breathing and increased snoring. In severe cases, where the adenoids block the nasal passage completely, they can cause sleep disturbances such as sleep apnea where breathing is stopped altogether. A child may be tired all the time as a result of interrupted sleep related to the nasal blockage which typically worsens at night.
The ideal treatment for chronically enlarged, obstructing adenoids and tonsils is to surgically remove them. However in many cases if a child develops a nasal breathing habit, the tonsils and adenoids shrink substantially often negating the need for surgery.
We also know that chronic nasal blockage can contribute to increased rates of ear infections and persistence of fluid in the middle ear area. For the child with recurrent ear infections, removal of enlarged and obstructing adenoids may help reduce the number of ear infections.
Of course enlarged adenoids are not the only cause of persistent nasal congestion in children. Aside from the history of symptoms, the best way to assess the size and condition of the airway is for the dentist to take a Cone Beam CT Scan of the head and neck region. These in-office scans take 90 seconds and are painless to the patient. The information gleaned from this technology is very important. The information includes:
- The accurate volume and dimension of the patient’s airway
- If changes in growth of the facial bones have occurred and to what degree.
- If congestion of the various sinuses is present
- What stage of growth and development the child is undergoing and to what degree can the growth changes be corrected by intervention.
- Head posture and alignment of the upper spine
The child’s dentist working closely with an ENT (Ear, Nose and Throat Specialist) can help to assess and eliminate the causative factors of facial growth abnormalities. When corrected early in a child’s life, the facial growth is encouraged to return to harmonious growth and development. In those cases where facial growth changes are significant and facial harmony is disrupted, the dentist may intervene and guide the child’s growth back to normal. Using various oral appliances, the dentist can actually modify the abnormal growth pattern and restore the balance of growth that nature intended.
The patient in the picture below, was treated with a Fixed Guided Growth Appliance for 4 months and then braces. You can see the correction of the facial asymmetry is profound and also the appliance created adequate space for all the teeth.
Taking your child to the dentist as early as possible, yes even at age 3, is very important. Here are four advantages of early examination, diagnosis and treatment:
- Removes harmful factors influencing growth
- Excellent ages for growth guidance and restoring normal growth
- Assists in improving the psychological well-being of the child
- Saves some patients from future jaw surgery
If you have a concern about your child’s ability to breathe, or rate of growth and development discuss it with your dentist or otolaryngologist. If you would like to speak to Dr. Stephen Deal about these aspects of your child’s health, you can make an appointment for evaluation by calling (501) 500-5105.

Diplomate, American Board of Craniofacial Pain
Senior Instructor, International Association for Orthodontics
Editorial Consultant, International Journal of Orthodontics
Diplomate, The Facial Beauty Institute
Master Senior Instructor, The Facial Beauty Institute
Fellow, International Association for Orthodontics
Fellow, Academy of General Dentistry
Fellow, American Orthodontic Society
Certified Dental Educator